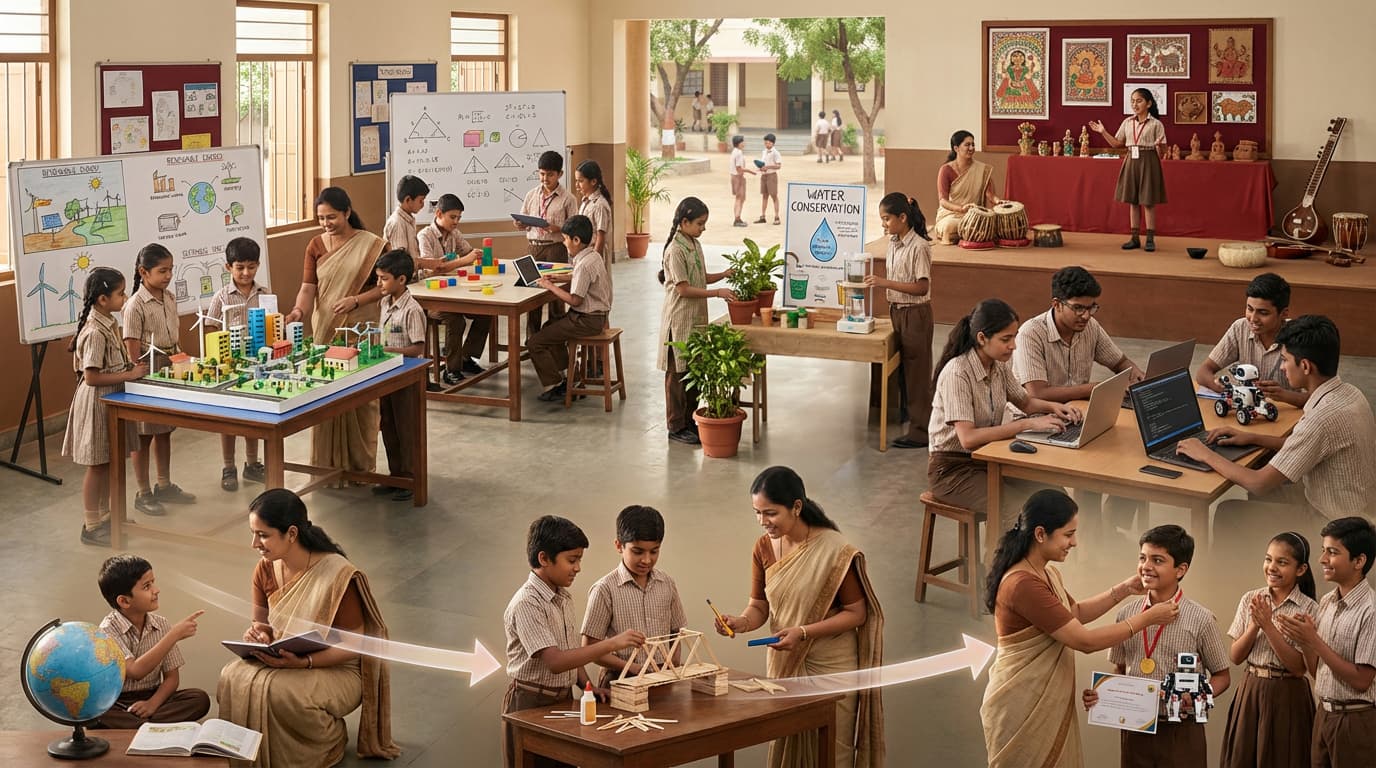
As education systems evolve, the purpose of schooling is being redefined. It is no longer enough for students to know concepts; they must also be able to apply knowledge, solve real problems, collaborate, and adapt. In response to this shift, CBSE has mandated the setting up of Composite Skill Labs (CSLs) in all affiliated schools, a move towards more experiential and skill-oriented learning. (CBSE Circular on Composite Skill Labs, 2025)
A Composite Skill Lab is a school-based, multi-purpose facility with equipments and machinery that enables students to learn and practise a range of skills through hands-on, project-based, and real-world activities.
Why are Composite Skill Labs necessary in schools?
a) Alignment with NEP 2020 and the NCF-SE 2023
National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 calls for a fundamental shift away from rote memorisation and content-heavy curricula towards competency-based learning, where curriculum content is reduced to its core essentials to allow space for critical thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge (NEP 2020, Sections 4.5–4.6). The policy further emphasises the adoption of experiential, inquiry-based, discovery-based, and project-based pedagogies as standard practice across all stages of schooling, with explicit attention to hands-on learning and exploration of connections across subjects (NEP 2020, Section 4.6).
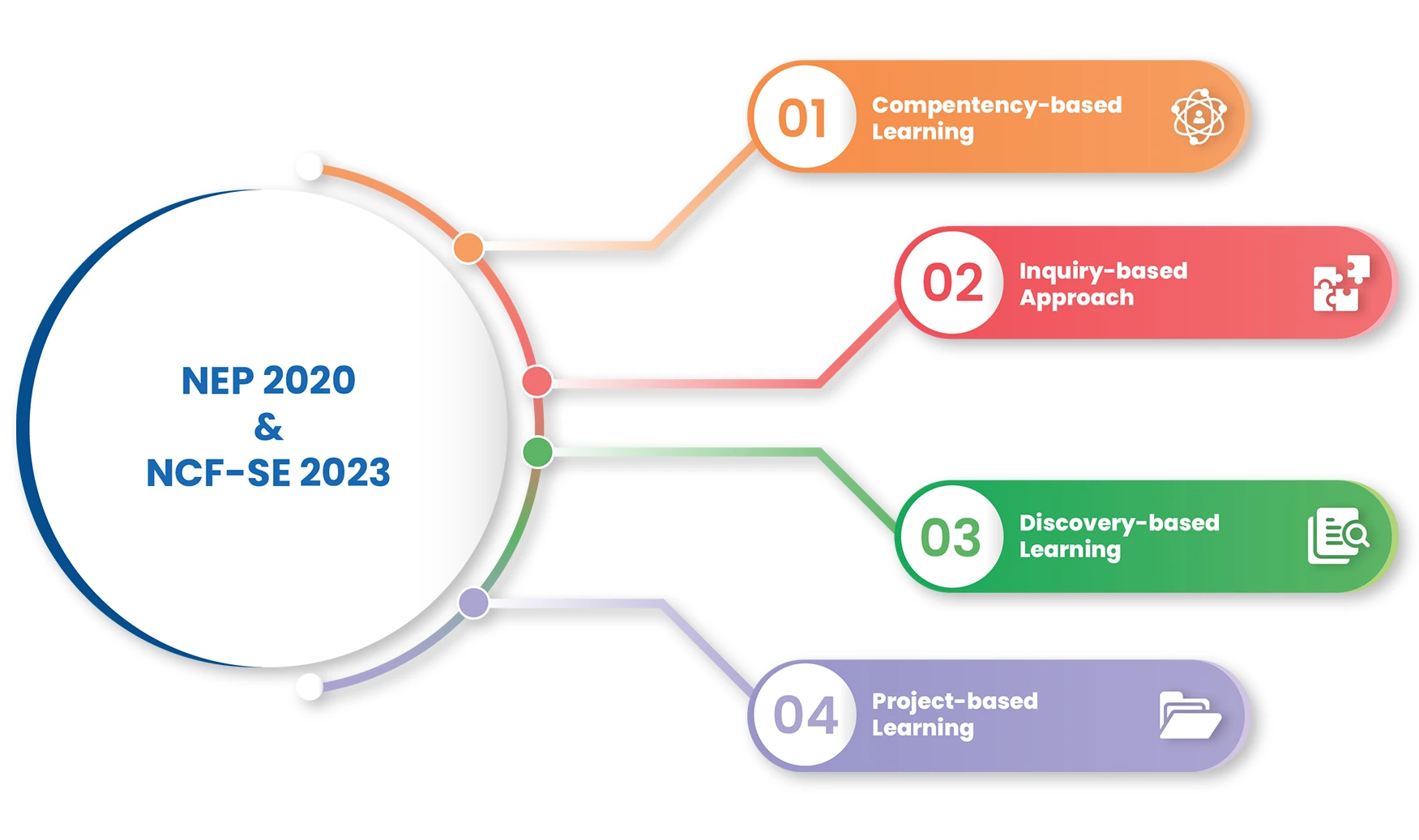
The National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF-SE) 2023 mandates the integration of skill education into the curriculum from the middle school stage onwards, with emphasis on real-world tasks, projects, and practical activities to facilitate application of learning.
CSLs translate these policy and curriculum mandates into action at the school level. By providing dedicated, well-equipped spaces, CSLs enable experiential and project-based learning to become a regular and structured part of everyday schooling.
b) Strengthening Teaching–Learning Practices and Student Outcomes
The mandate for CSLs stems from a growing recognition that content-heavy, exam-focused education alone cannot prepare learners for the complexities of modern life and work.
Research shows that students develop deeper understanding and transferable skills when they work on authentic tasks, collaborate with peers, apply concepts across disciplines, and reflect on their learning processes (Thomas, 2000; Hmelo-Silver, 2004; OECD, 2018).
CSLs provide the physical and pedagogical infrastructure required to embed these practices within regular school curricula. They support the integration of skill education into the regular curriculum by bridging theory with practice and exposing students to vocational, industry-relevant, and entrepreneurial skills, as envisioned in NEP 2020.
At the school level, CSLs offer several long-term benefits. They are intended to expose students to practical skills aligned with industry needs and real-world work environments, thereby building early career awareness and confidence (CBSE, 2024). Studies indicate that through collaborative and practical tasks, students develop essential 21st-century skills such as critical thinking, communication, creativity, and teamwork, which are required for both higher education and employment (OECD, 2018).
Research also highlights that when learning is connected to real-world contexts and practical application, students demonstrate higher levels of engagement and deeper understanding. Such engagement is associated with improved persistence in learning. (Thomas, 2000). CSLs support this by providing structured opportunities for students to apply academic concepts in meaningful and hands-on contexts.
Implementing Composite Skill Labs Effectively
Setting up a CSL is not just about infrastructure; it is about effective implementation.
Some practical considerations include:
- Aligning CSL activities with curriculum goals and learning outcomes
- Starting with simple, well-designed projects and scaling gradually
- Encouraging cross-subject collaboration and teamwork
- Using student portfolios, reflections, and presentations for assessment
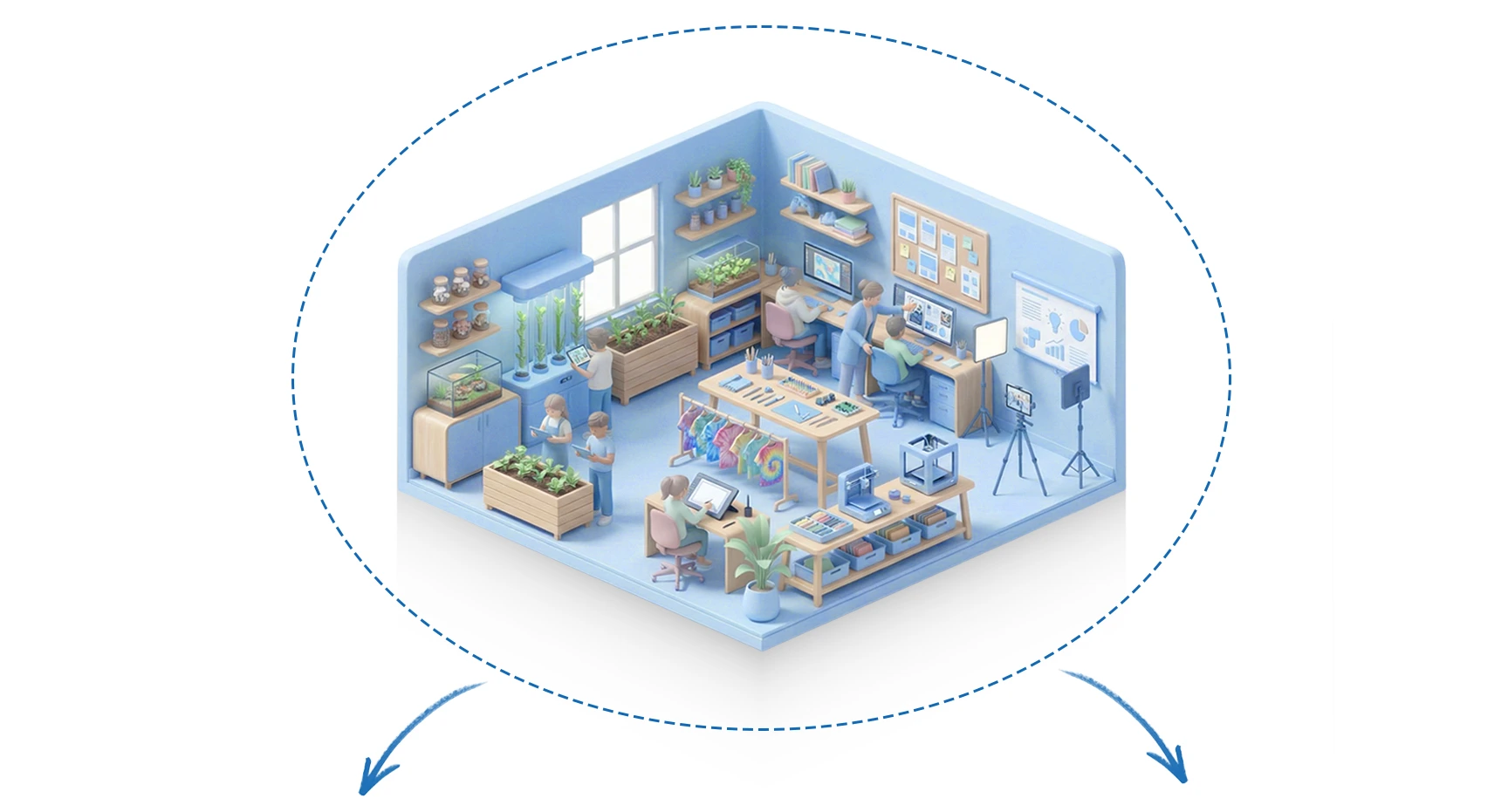
Infrastructure and Space Requirements
As per CBSE guidelines, schools are advised to set up:
- One Composite Skill Lab of 600 sq. ft. for classes VI–XII, or
- Two separate labs of 400 sq. ft. each — one for Classes VI–X and the other for Classes XI–XII
These labs should be equipped with appropriate tools, equipment, and machinery to support hands-on, skill-based, and project-oriented learning across disciplines.
Implementation
Timeline
- For schools seeking fresh CBSE affiliation:
Setting up a Composite Skill Lab with all necessary equipment is a mandatory prerequisite for affiliation. - For schools already affiliated with CBSE:
Schools are required to establish a Composite Skill Lab within three years from the date of the CBSE circular.
CSLs represent a significant step towards future-ready education. They translate the vision of NEP 2020 and NCF-SE 2023 into classroom practice by enabling experiential and skill-based learning.
When implemented thoughtfully, CSLs can transform schools into spaces where students do not just learn concepts but apply, create, and innovate, thereby preparing them not only for exams but also for life beyond school.
References
- Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). Circular on Composite Skill Labs, 2024.
- Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). Circular on Composite Skill Labs, 2025.
- Hmelo-Silver, C. E. (2004). Problem-Based Learning: What and How Do Students Learn? Educational Psychology Review.
- Ministry of Education, Government of India. National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Ministry of Education, Government of India. National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF).
- OECD (2018). The Future of Education and Skills: Education 2030.





